Kamailio for beginners
1) Kamailio is SIP proxy which routes only SIP packets and it is doing nothing with media. Let’s take a look on SIP call. SIP call we can divide in 2 parts: media and signaling. Media is audio or video for a call, signaling is a requests and responses for call initialization, call forwarding and etc. With SIP you can do audio, video calls, instant messaging and etc. Simple call flow with Kamailio:
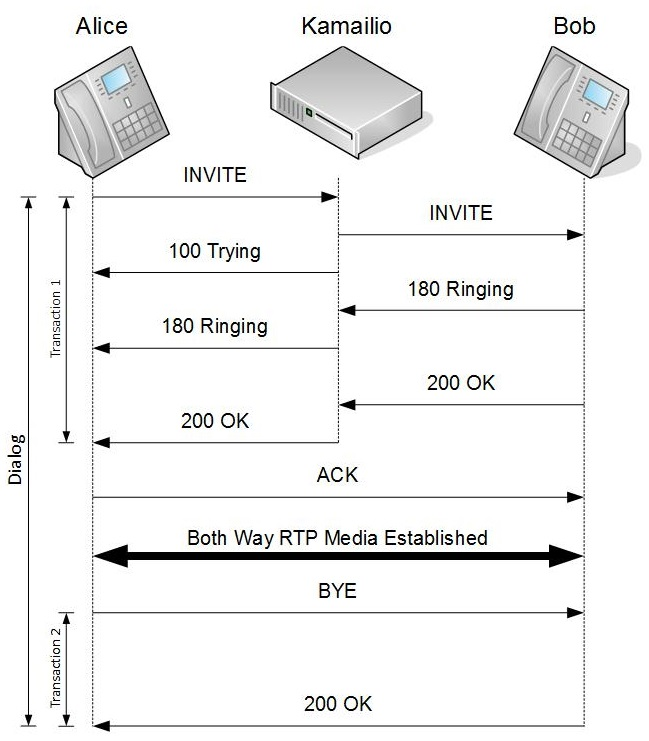
Above call flow is just one possible way to establish a call using SIP proxy, in some other cases you might want to have all SIP requests to be passed through Kamailio including ACK and BYE. Kamailio will handle only SIP request and responses(Invite, Ack, Trying, …), below you can find example for INVITE request sent from Alice to Proxy:
INVITE sip:bob@biloxi.example.com SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/UDP client.atlanta.example.com:5060;branch=z9hG4bK74bf9
Max-Forwards: 70
From: Alice <sip:alice@atlanta.example.com>;tag=9fxced76sl
To: Bob <sip:bob@biloxi.example.com>
Call-ID: 2xTb9vxSit55XU7p8@atlanta.example.com
CSeq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:alice@client.atlanta.example.com>
Content-Type: application/sdp
Content-Length: 151
v=0
o=alice 2890844526 2890844526 IN IP4 client.atlanta.example.com
s=-
c=IN IP4 192.0.2.101
t=0 0
m=audio 49172 RTP/AVP 0
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000More details regarding SIP response and requests you can find online.
2) Kamailio is great application which can handle millions sip messages and can support thousands of simultaneous calls. Kamilio is used by: Telio, Orange, Sipgate and etc. Kamailio is build as modular application and it contains 200+ modules.
3) Kamailio installation is very straight forward, to install kamailio you can use following manual: https://www.kamailio.org/wiki/install/4.4.x/git At the end you should have fully functional Kamailio which you can start using straightaway, no other changes is necessary to config file.
4) Kamailio main configuration file is /usr/local/etc/kamailio/kamailio.cfg
This file is very well prepared for using it straightaway. You can turn on or off several features in this file without major changes in config file.
To turn on user authentication using MySQL you can put following lines at the top of config file(if you installed kamailio using link provided above,
then authentication using MySQL you probably turned on):
#!define WITH_MYSQL !define WITH_AUTH
#!define WITH_USRLOCDBAdditionally you can turn on several other features:
#!define WITH_NAT WITH_NAT will need you to install RTPProxy, but in this case you will be able to support user-agents or phones behind NAT. RTPProxy will bridge media for clients.
#!define WITH_PSTNWITH_PSTN - will allow you to send calls to SIP gateway in case if you need to call out from your Kamailio to somewhere else. Just enabling it will not be enough, but you will need to add ip address and port in config, for example you will need to add PSTN gateway 10.0.0.101:5060
pstn.gw_ip = "10.0.0.101" desc "PSTN GW Address"
pstn.gw_port = "5060" desc "PSTN GW Port"#!define WITH_DEBUGWITH_DEBUG - will increase debug level and you will able to see more chatty log outputs in default stderr.
This mean if you before was looking for logs in /var/log/syslog or /var/log/messages now you will not see there anymore. :)
The logs should be outputted in your terminal window if you started kamailio using simillar command:
/usr/local/sbin/kamailio -f /usr/local/etc/kamailio/kamailio.cfg -DDIf you need more chatty messages in log file, then you might change following lines accordingly:
#!ifdef WITH_DEBUG
debug=4
log_stderror=no # this line should be changed, no is for writing logs to rsyslog file even when WITH_DEBUG is enabled
#!else
debug=2
log_stderror=no
#!endifAdditionally you might increase or decrease debug values from 1 to 4, higher value for more debug.
5) Kamailio config has 3 parts: global settings, modules settings and routing blocks. In global settings part you can define WITH_DEBUG for example, configure ports, ip-addresses and protocols on which kamailio is listening. In module part are listed all used modules and listed modules configurations. In routing part there is several routing blocks.
All request first hit request_route and from there they might jump to other routes like:
route[PSTN]. To jump to PSTN route you need to use route(PSTN); command from request_route.
If sub-routes are not finished with exit or drop command, then it returns back to route from where it was invoked,
you can put return command at the end of sub-route and it is almost the same behavior.
6) t_relay() function will send out SIP request out of Kamailio. If you have any failure routes, then this failure routes will be executed inside this function.
sl_send_reply() function will send reply. For example if request URI is empty we reply that address is incomplete:
if ($rU==$null) {
# request with no Username in RURI
sl_send_reply("484","Address Incomplete");
exit;
}All responses will hit reply_route, where we can either drop reply or to forward it.
7) AVP is an array(but let assume it is simple variable so we are not confused with all flexibility) which attached to SIP transaction. In case if we need to save some value and later on we can use it during same transaction, for example in default config we will save user from request URI:
$avp(oexten) = $rU;And later we can access it when we will send call to VM:
$ru = "sip:" + $avp(oexten) + "@" + $sel(cfg_get.voicemail.srv_ip)
+ ":" + $sel(cfg_get.voicemail.srv_port);There is some additional rules when you can access AVP, if AVP for example was created in request_route then it will be accessible in branch_route,
failure_route or onreply_route. There is some additional rules where AVP can be created and where it can be accessible, but lets skip it for today.
There is XAVPs too, where x stands for extended, but we will not discuss this today.
There is several predefined variables like $ru what is request uri or $rU what stands for user in request URI.
$var(x) is variable stored in private memory and this variable is preferable to use for temporary operations.
It is persistent in process of Kamailio and is not reset or attached into transaction. Keep in mind that Kamailio will have several different
processes and this variable is not shared between then. If you need to share variable between kamailio processes then you should use shared variable $shv(x).
$fu stands for From URI, $fU stands for user in From URI. There some other variables related to from URI.
In case if you need to update $fu or $fU, you need keep in mind that Kamailio will update them only when it will send it out.
To update immediately you can use msg_apply_changes() command.
Lets assume $fu is bbb, then:
$fu=”aaa”;
if($fu==”aaa”) {
# execution never go here
}Lets assume $fu is bbb, then:
$fu=”aaa”;
msg_apply_changes();
if($fu==”aaa”) {
# execution will go here
}It is not recommended to use msg_apply_changes() very often, cause it may impact performance. It is recommended to use uac_replace_from() function for updating caller-id.
8) Kamctl is powerful tool and below you can find my most common used commands.
kamctl fifo debug #will return current debug level.
kamctl fifo debug 4 #will increase debug level to max without restart.
kamctl dispatcher dump #will show dispatcher list loaded in memory.
kamctl dispatcher reload #will reload dispatcher list
kamctl add test testpasswd #will add user test with password testpasswd
kamctl db show subscriber #will show all users what are in DB
kamctl rm test #will remove user test
kamctl ul show #will show registered users